peelable shims
Shims are slices of metal or plastic material used to fill space between two objects or faces of objects. They are used for leveling, for adding support, or adjusting for a better fit. While some shims are wedge shaped to make them easier to install, machined shims are usually flat, with tight tolerances. They are available in a variety of styles and configurations to accommodate almost any application. While shim rings and washers have the same appearance and some shims are even called washers, the two have very different functions — washers are designed to take and spread loads, while shims fill space.
Design Considerations
Washers vs. Shims
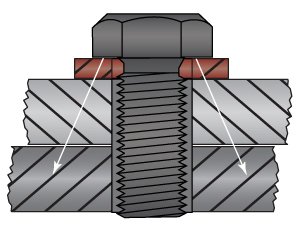
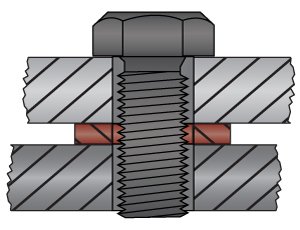
While both are used to protect machined components, reduce vibration, or act as a sound buffer, washers spread the load of a bolt or screw, and shims take up space and align parallel and angled surfaces of interfacing elements.
Left:
Washers are stamped, leaving a rollover edge and breakout edge. Washers cost less than shims.
Right:
Shims have smooth corners, flat edges, and parallel faces. Very flat with consistent thickness.
For best results, wall thickness for shims should be at least three times the material thickness.
Preventing Wear
If the hardness of the shim and component faces do not match, the softer face will be subjected to excessive wear. For best results, and to save time and money on rebuilds, shims should be designed into applications to prevent contact between expensive components.
Measuring Space
A set of feeler gauges (or leaf gauge) can be very handy to determine the amount of space that needs to be shimmed.
Shim & Spacer Types
Arbor Shims
Also known as shim rings, arbor shims are made from precise materials with specific tolerances. They are used for spacing and alignment.
Arbor Spacers
The inside diameter of an arbor spacer features a key way that slides over a shaft and machine key during installation. A wide range of sizes and thicknesses allow accurate alignment and spacing.
Shim Washers (DIN 988)
Full hard low carbon and spring steel metric DIN 988 shim washers are supplied in two styles: PS and SS. SS support rings are thicker and harder than PS shim washers.
Collars
Collars are similar to arbor spacers. A key way cut into the inside diameter slides over, and turns with, shafts and machine keys to precisely position arbors in milling machines, saws, and grinders.
Lengthening
Lengthening shims fit over the screw threads and under the shoulder of stripper bolts, which, in effect, lengthens the stripper bolt length.
Shortening
Shortening shims fit over the shank, just under the head of a stripper bolt, shortening the effective length of the bolt.
Laminated
Laminated shim rings have the added feature of peelable layers which can be removed until the desired thickness is achieved.
Slotted
Slotted shims are an efficient way to solve alignment and leveling problems because they do not have to be hand cut. They are used on assembled machine components in order to maximize alignment and balance.
Stock
Shim stock is available in flat sheets, laminated flat sheets, and rolls in a variety of materials to fit your need. It can be cut in the field to fit your application.
Design & Use
Slotted Shims for Machine Alignment

Slotted shims are used to align machinery and are installed around anchor bolts that connect to motor mounts. Typically the machine is lifted or tilted while the shims are slid into place near motor mounts. In most cases the anchor bolt is straddled on either side through the shim slot.
It is important for the slot to completely straddle the threads so as not to interfere with threads during torquing, and to prevent distortion of the shim. The tab of the shim is used to prevent the opportunity for the installers fingers to be crushed when the machine is lowered onto the mounts. The best method of installation is to slide the shim and straddle the anchor bolt until you can feel it touching, then withdraw the shim a small amount (approx. 1 mm) to ensure clearance of the threads.
An improperly mounted motor may cause significant damage to the motor house, mounts, and adjoining components.
Shimming the mounts provides a repeatable alignment preventing damage to valuable equipment.
Shim Selection Guidelines
For best results, do not use more than four shims in one setting.
Sandwich thinner shims between thicker shims for protection.
Never shim more than an overall elevation of .150″
Quick Reference Guide
Shims are a class of materials used for spacing and alignment. Made with precise materials and production techniques, shims are available in a variety of styles and materials to suit your needs.
Arbor Shim
Common Names:
Shim, Slitter Shim, Shim Washer
Applicable Standards:
None known
Fabrication:
Most commonly made from high carbon steel, also known as blue tempered, stainless steel, or brass. Other materials not standard, but are used.
How to Identify:
Outside diameter x inside diameter x thickness.
Common Uses:
Used for fast, accurate spacing of milling cutters, gang cutters, saws, slitting blades, and grinding tools.
Comments:
Some versions made from 1010 full hard material, which is more pliable but has less wear properties than blue tempered.
Arbor Spacer
Common Names:
Keyed Spacer, Arbor Shim
Applicable Standards:
Other than matching standard key way sizes, no standards are known.
Fabrication:
Most commonly made from high carbon steel, also known as blue tempered, stainless steel, or brass. Other materials not standard, but are used.
How to Identify:
Outside diameter x inside diameter x thickness.
Common Uses:
Used to fit arbors onto various types of small machine tools, including grinders. Key way aligns to the mating key ways of mating components.
Comments:
There is a thicker version that is produced from machined parts known as a keyed spacer.
Shim Washer
Common Names:
Shim Washer, PS Shim Washer
Applicable Standards:
DIN 988 PS series
Fabrication:
Usually stamped from shim steel (1045 – 1075). Standard sizes generally 0.25 – 1.0 mm thick, though range is 0.15 – 1.9 mm. ID and OD generally expressed in increments of 0.1 mm.
How to Identify:
Outside diameter x inside diameter x thickness.
Common Uses:
Primary purpose is to take up axial play between machine components. Shim washers are common components in gear boxes and gearing systems.
Comments:
Generally much less expensive than DIN 988 SS series. No imperial standards.
Shim Support Washer
Common Names:
Support Washers, Support Rings, SS Shim Ring, Backup Ring
Applicable Standards:
DIN 988 SS series
Fabrication:
Usually stamped from spring steel to HRC 44 – 49. Larger sizes sometimes machined from tubing with ground side faces.
How to Identify:
Outside diameter x inside diameter x thickness.
Common Uses:
Used between machine components. Often used to provide a flat and solid surface for a retaining ring that retains components against a shaft.
Comments:
Generally much more expensive than DIN 988 PS series due to more precision in manufacturing. No imperial standards.
Spacer / Collar
Common Names:
Slitter Spacer, Arbor Spacer, Arbor Collar
Applicable Standards:
While there are no known standards, thicknesses and tolerances are aligned with industry norms.
Fabrication:
Usually hardened and ground parallel and perpendicular. Lapped for parallelism. Edges are chamfered.
How to Identify:
Most often specified to an application using a blueprint. Mostly custom parts.
Common Uses:
Used for spacing and as collets for machined components on shafts.
Comments:
Generally a custom fabricated part.
Lengthening / Shortening
Common Names:
Variable Shim, Lengthening Shim, Shoulder Screw Shim, Stripper Bolt Shim
Applicable Standards:
None known, though ID and OD match the mating dimensions of a stripper bolt.
Fabrication:
Stamped from spring steel, or medium to high carbon grades, 1045 – 1095.
How to Identify:
Screw/bolt size x thickness.
Common Uses:
Used to increase the effective length of shoulder bolts/stripper screws by installing over the threads but remaining beneath the stepped shaft of the stripper bolt.
Comments:
Stripper bolts are used in tool and die work to hold stripper plates in place. Stripper plates guide the punch tip in a stamping operation and this controlling parallelism is important.
Laminated
Common Names:
Laminated Shim, Variable Shim, Adjustable Shim, Peel Off Shim
Applicable Standards:
CDA‑260 half hard brass material is most common, but also made from aluminum, steel, and stainless steel.
Fabrication:
Shim layers are bonded together with pressure and resin or adhesive.
How to Identify:
Inside diameter x thickness.
Common Uses:
Allows for progressive shimming and adjustment of machine components. Especially useful in blind or recessed applications, or where there are concerns for contaminants between layers.
Comments:
Layers can be peeled away with a pocket knife. Eliminates need to stack shims together and prevents contamination between shims.
Slotted
Common Names:
Slotted Shim, Horseshoe Shim, Slotted Motor Shim
Applicable Standards:
Stainless steel and platic are most common. Sizes are called out using letters representing the squared dimensions of the slot.
Fabrication:
Designed with a bolt slot to ease installation. Stainless steel is most common.
How to Identify:
Size code x thickness.
Common Uses:
Used to level motors and machinery, especially to ensure the alignment of components, such as a motor to a pump.
Comments:
The tab allows for safe installation without risk to operator to crush fingers. Do not shim more than .150″ and use thicker shims on either side of thin shims to minimize wear.
Shim Stock

Common Names:
Shim Stock, Shim Rolls, Rolled Shim
Applicable Standards:
While there are no known standards, thickness tolerances are carefully controlled, as is the material content.
Fabrication:
Rolled or flat sheets. Rolled is more economical to manufacture, ship, and store, though flat sheets tend to work better when trying to cut a large piece to size, as the rolls tend to want to reroll and not stay flat until installed.
How to Identify:
Length x width x thickness.
Common Uses:
Primary use is in tool and die alignment. Also used for automotive and truck axle shims.
Comments:
Color coded plastic stock eliminates need to check thickness with a micrometer. Custom cut edges need to be deburred before installation.
Standard Sizes
Shim sizing is proportional to the size of the anchor bolts and can be estimated based on the horsepower of the machine:
Estimated Shim Sizes and Horsepower Ranges
| Shim Dimensions | Horsepower Range | |
|---|---|---|
| Size A | 2″ x 2″ with 9/16″ slot | 0.25 – 15 |
| Size B | 3″ x 3″ with 13/16″ slot | 10 – 60 |
| Size C | 4″ x 4″ with 1-3/16″ slot | 50 – 200 |
| Size D | 5″ x 5″ with 1-9/16″ slot | 150 – 1,000 |
Motor Frame Sizing
There are some standard shim sizes based on standard motor frame numbers. The following table serves as a guide:
Motor Frame Numbers
| Size A | Size B | Size C | Size D | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2″ x 2″ x 9/16″ | 3″ x 3″ x 13/16″ | 4″ x 4″ x 1-3/16″ | 5″ x 5″ x 1-9/16″ | ||||
| 42 | 184 | 66* | 325 | 203* | 408 | 502 | 681 |
| 48 | 185 | 253 | 326 | 204* | 409 | 503 | 682 |
| 56 | 186 | 254 | 327 | 224* | 443 | 504 | 683 |
| 143 | 187 | 255 | 328 | 225* | 444 | 505 | 684 |
| 145 | 188 | 256 | 329 | 363 | 445 | 506 | 685 |
| 162 | 189 | 257 | 364 | 446 | 507 | 686 | |
| 163 | 1810 | 258 | 365 | 447 | 508 | 687 | |
| 164 | 213 | 259 | 366 | 448 | 509 | 689 | |
| 165 | 214 | 283 | 367 | 449 | 582 | ||
| 166 | 215 | 284 | 368 | 504* | 583 | ||
| 167 | 216 | 285 | 369 | 505* | 585 | ||
| 168 | 217 | 286 | 403 | 506* | 586 | ||
| 169 | 218 | 287 | 404 | 507* | 587 | ||
| 1610 | 219 | 288 | 405 | 508* | 588 | ||
| 182 | 2110 | 289 | 406 | 509* | 589 | ||
| 183 | 323 | 407 | |||||
| 324 | |||||||