Progressive cavity pumps are widely used in various industries due to their ability to handle viscous fluids and deliver a steady flow. Understanding the pump curves associated with these devices is essential for optimizing their performance and ensuring efficient operation. This article will explore the key aspects of progressive cavity pump curves, including their significance and interpretation.
What Are Pump Curves?
Pump curves are graphical representations that illustrate the performance characteristics of a pump. They typically display the relationship between flow rate and head, along with other important parameters like efficiency and power consumption. For progressive cavity pumps, these curves help users understand how the pump will perform under different operating conditions.
Key Components of Progressive Cavity Pump Curves
- Flow Rate: This is the volume of fluid that the pump can move over a specific period. It is usually represented on the horizontal axis of the curve.
- Head: Head refers to the height that the pump can lift the fluid. It is typically plotted on the vertical axis and indicates the energy imparted to the fluid.
- Efficiency: This curve indicates how effectively the pump converts mechanical energy into fluid energy. Higher efficiency means lower operational costs.
- Power Consumption: This component shows the amount of power required to operate the pump at various flow rates.
Interpreting the Pump Curve
To effectively use progressive cavity pumps curves, one must be able to interpret them accurately. Here are some essential tips:
- Determine Operating Point: The intersection of the system curve and the pump curve indicates the operating point. This is where the pump will function optimally.
- Analyze Efficiency: Look for the efficiency curve to find the flow rate that provides the best performance. Operating too far from this point can lead to energy waste.
- Assess Head: Ensure that the pump can provide adequate head for your application. If the required head exceeds the pump’s capability, it may not function correctly.
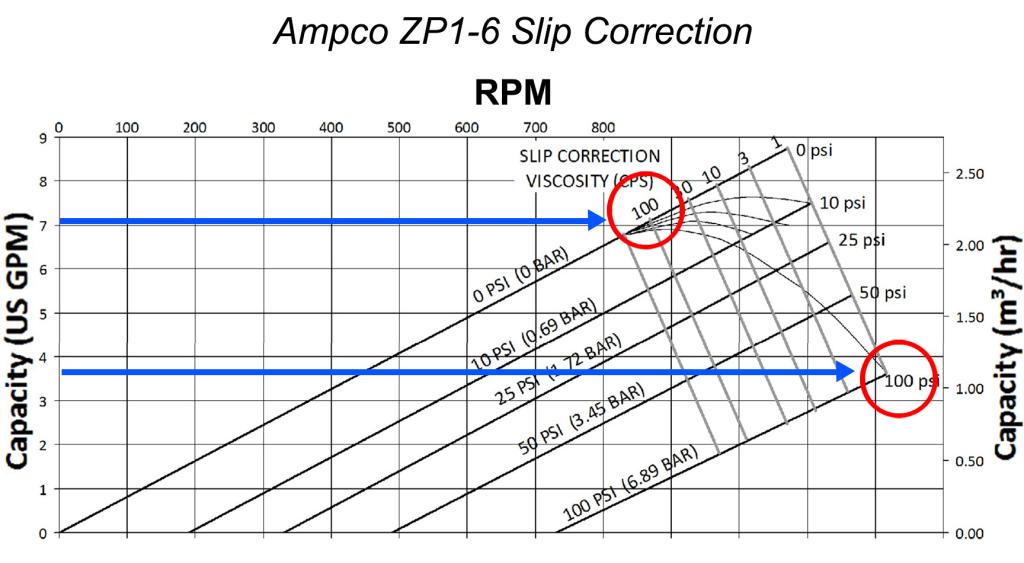
- Consider Viscosity: Progressive cavity pumps excel in handling viscous fluids. However, viscosity can affect the pump’s performance, so it’s crucial to consider this when reading the curves.
Factors Influencing Pump Performance
Several factors can impact the performance of progressive cavity pumps, which should be taken into account when analyzing pump curves:
- Fluid Characteristics: Properties such as viscosity, temperature, and density can significantly affect flow rates and efficiency.
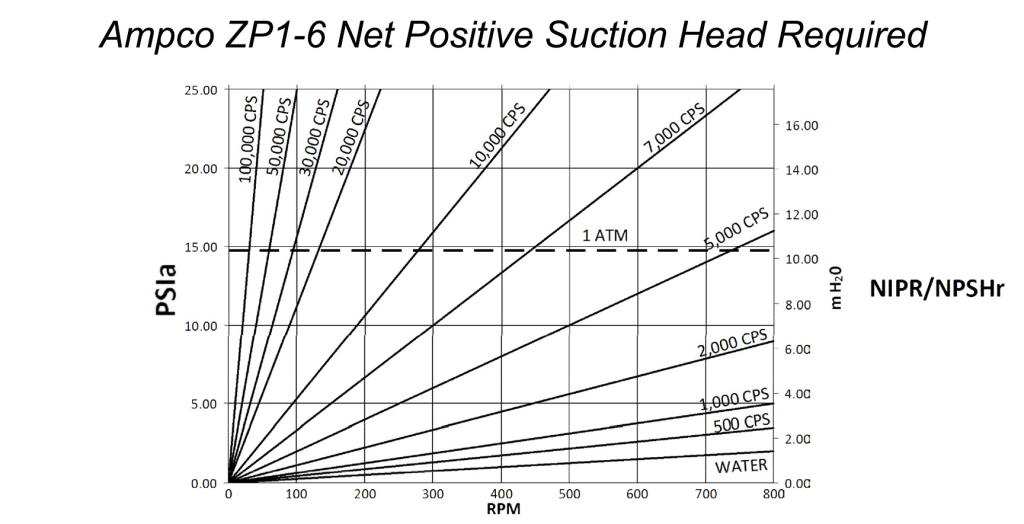
- Suction Conditions: Proper suction conditions are vital for maintaining performance and avoiding cavitation.
- Wear and Tear: Over time, components of the pump may wear out, impacting its curves and overall function.
Conclusion
Understanding progressive cavity pump curves is crucial for anyone involved in the selection and operation of these pumps. By familiarizing yourself with the key components and interpretation techniques, you can ensure that your pump operates efficiently and effectively. This knowledge not only helps in optimizing performance but also contributes to cost savings and improved system reliability.