Progressive cavity pumping is a reliable method for transporting viscous and shear-sensitive fluids in various industries. This ultimate guide covers everything you need to know about progressive cavity pumps, from their operation and design to applications, advantages, maintenance, and troubleshooting.

1. Introduction to Progressive Cavity Pumps
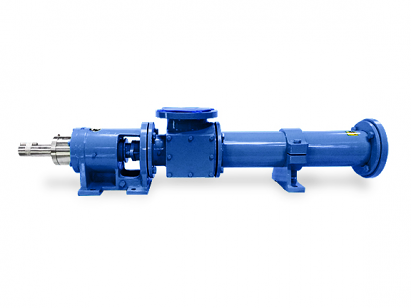
- Definition: A progressive cavity pump is a type of positive displacement pump that uses a helical rotor and stator to move fluids.
- Functionality: It creates a series of cavities that transport fluid through the pump as the rotor turns.
2. Working Principle
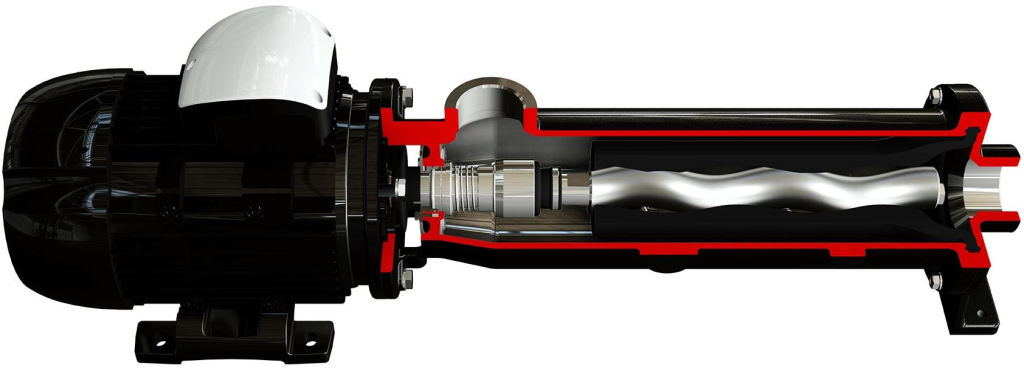
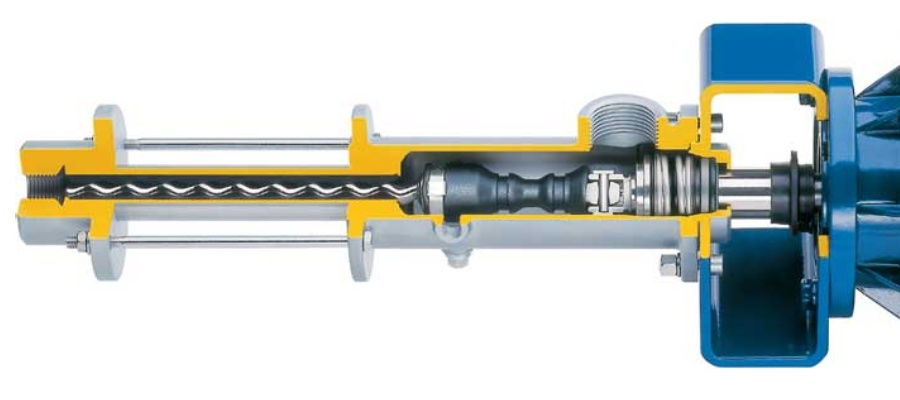
- Components:
- Rotor: A helical screw that rotates and creates cavities.
- Stator: A complementary helical element that forms a seal with the rotor, allowing for fluid movement.
- Operation:
- As the rotor turns, it creates a vacuum that draws fluid into the cavities.
- The fluid is then pushed through the pump and out through the discharge port, ensuring a continuous flow.
3. Advantages of Progressive Cavity Pumps
- Versatility: Can handle a wide range of fluids, including viscous, non-viscous, and those containing solids.
- Low Pulsation: Provides a steady flow with minimal pulsation, making it suitable for sensitive applications.
- Self-Priming: Capable of handling fluids with low NPSH and can pump fluids containing air or gas.
- Durability: Designed to withstand abrasive and corrosive materials with suitable construction materials.
4. Applications of Progressive Cavity Pumps
Progressive cavity pumps are used across various industries:
- Food Industry:
- Transporting slurries, pastes, and other viscous food products.
- Wastewater Treatment:
- Handling sludge, sewage, and thick fluids.
- Chemical Processing:
- Pumping corrosive and hazardous chemicals.
- Oil and Gas:
- Moving crude oil, drilling mud, and heavy fluids.
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Managing shear-sensitive formulations and active ingredients.

5. Design Considerations
- Material Selection:
- Choose materials that are resistant to corrosion and abrasion based on the fluid being pumped.
- Sizes and Configurations:
- Select appropriate pump sizes and configurations based on flow rate and pressure requirements.
- Drive Options:
- Consider electric or hydraulic drives depending on the application and available power sources.
6. Maintenance of Progressive Cavity Pumps
Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance:
- Lubrication: Ensure proper lubrication of all moving parts.
- Inspection: Regularly check seals and gaskets for wear and replace them as needed.
- Cleaning: Keep the pump clean to prevent buildup that could reduce performance.
- Alignment: Maintain proper alignment of the drive shaft.
7. Troubleshooting Common Issues
A. Insufficient Flow Rate
- Possible Causes:
- Clogged suction or discharge lines.
- Worn rotor or stator.
- Solutions:
- Inspect and clean lines.
- Replace worn components.
B. Increased Wear and Tear
- Possible Causes:
- Pumping abrasive materials.
- Incorrect material selection for the rotor and stator.
- Solutions:
- Use wear-resistant materials.
- Regularly check and replace components.
C. Leakage
- Possible Causes:
- Worn seals or gaskets.
- Solutions:
- Inspect seals and replace as needed.